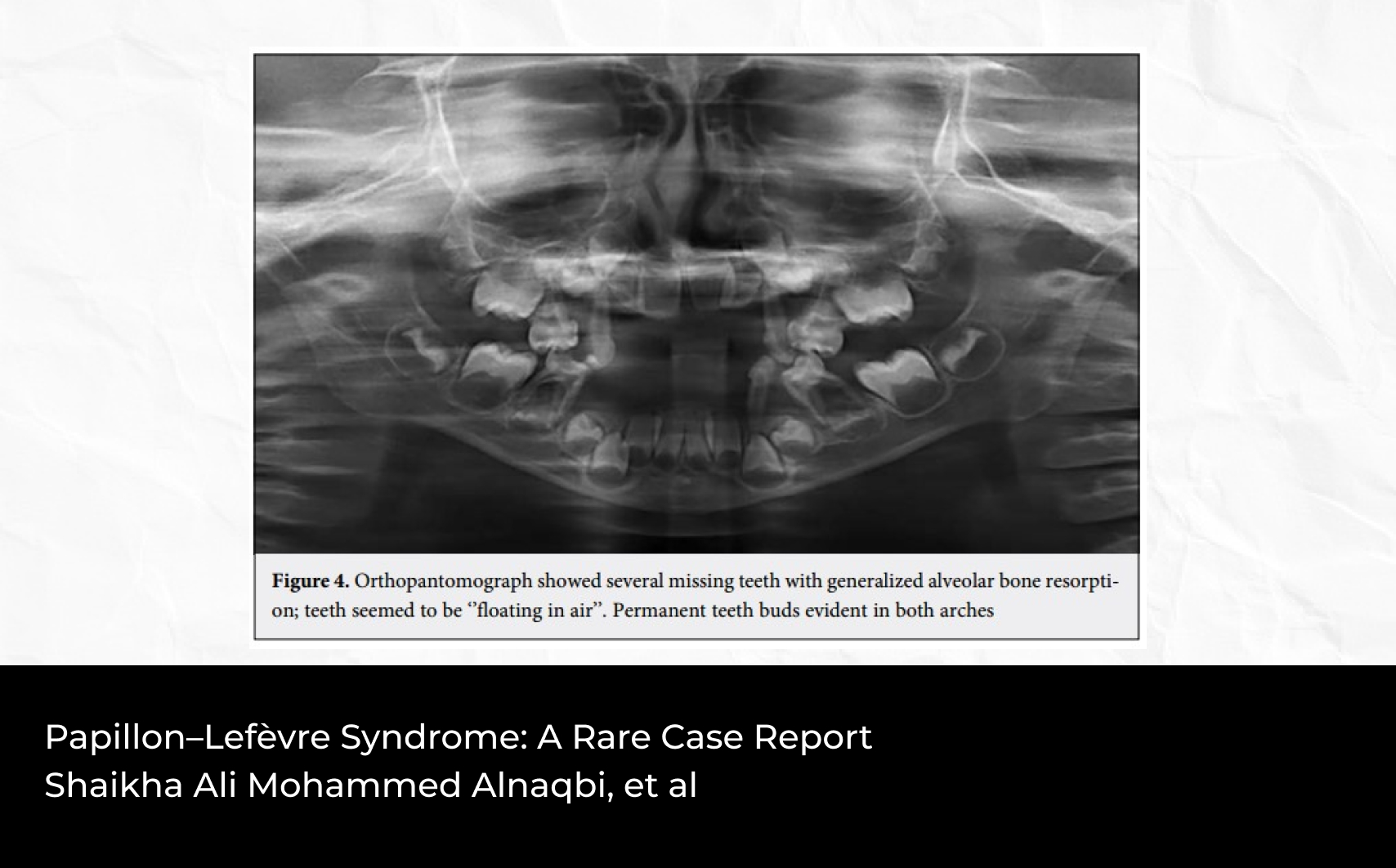
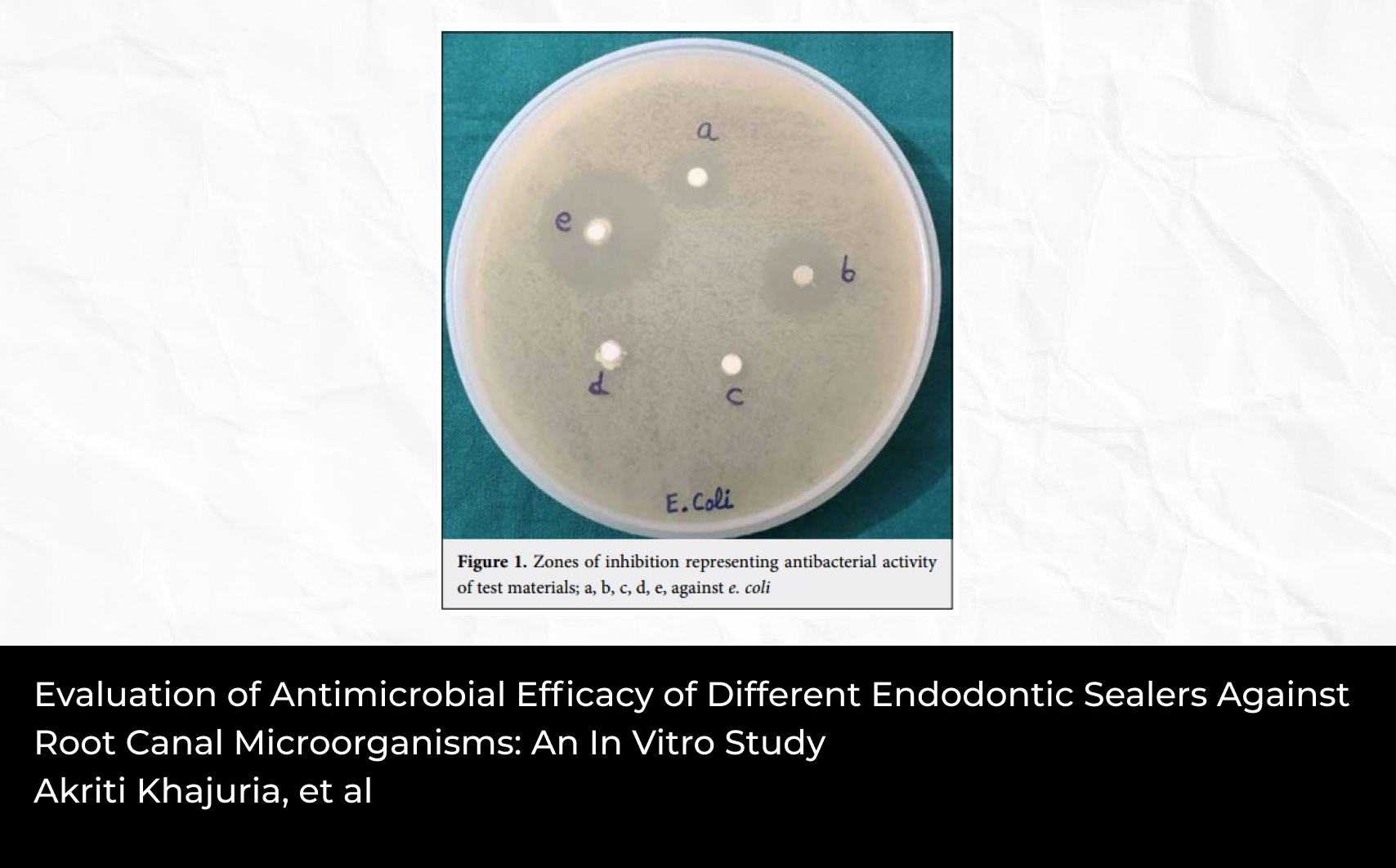
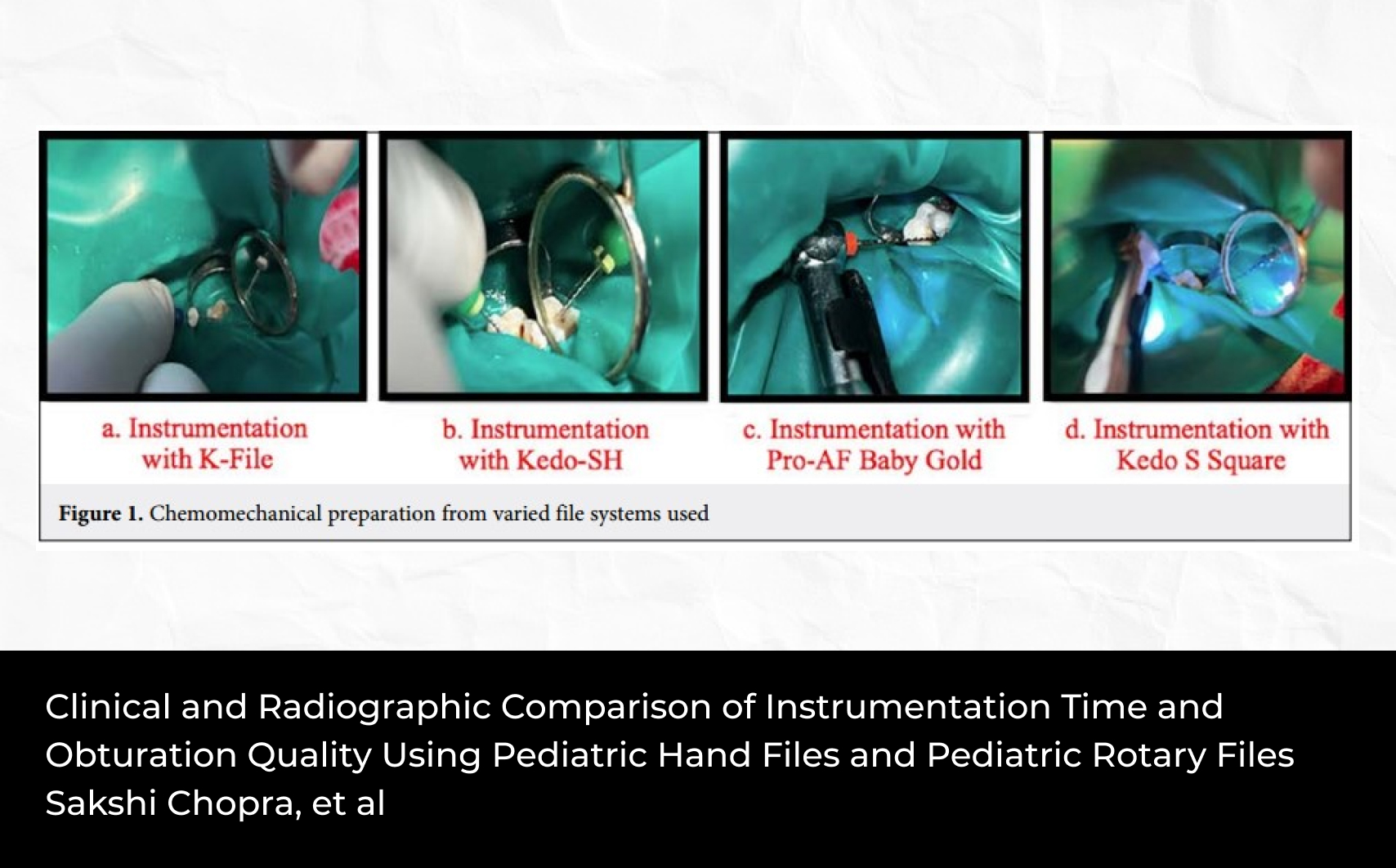
Abstract
Children infected with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) receive anti-retroviral therapy (ART) quite early in life. These drugs could possibly have an effect on tooth development. A group of 221 HIV-infected children in the age group of 6-18 years (mean 11.62 ± 3.30 years) were examined for any tooth anomalies. Only 109 children were on ART and they were divided into three groups based on the anti-retroviral regimen they received. Twenty percent of children on ART had microdontia of the first premolars, with a mean age of drug onset 3.2 ± 0.8 years. Type of anti-retroviral regimen and age of administration appears to have an effect on developing teeth. There is a need for further research on the possible effects of anti-retroviral medications on tooth mineralization.