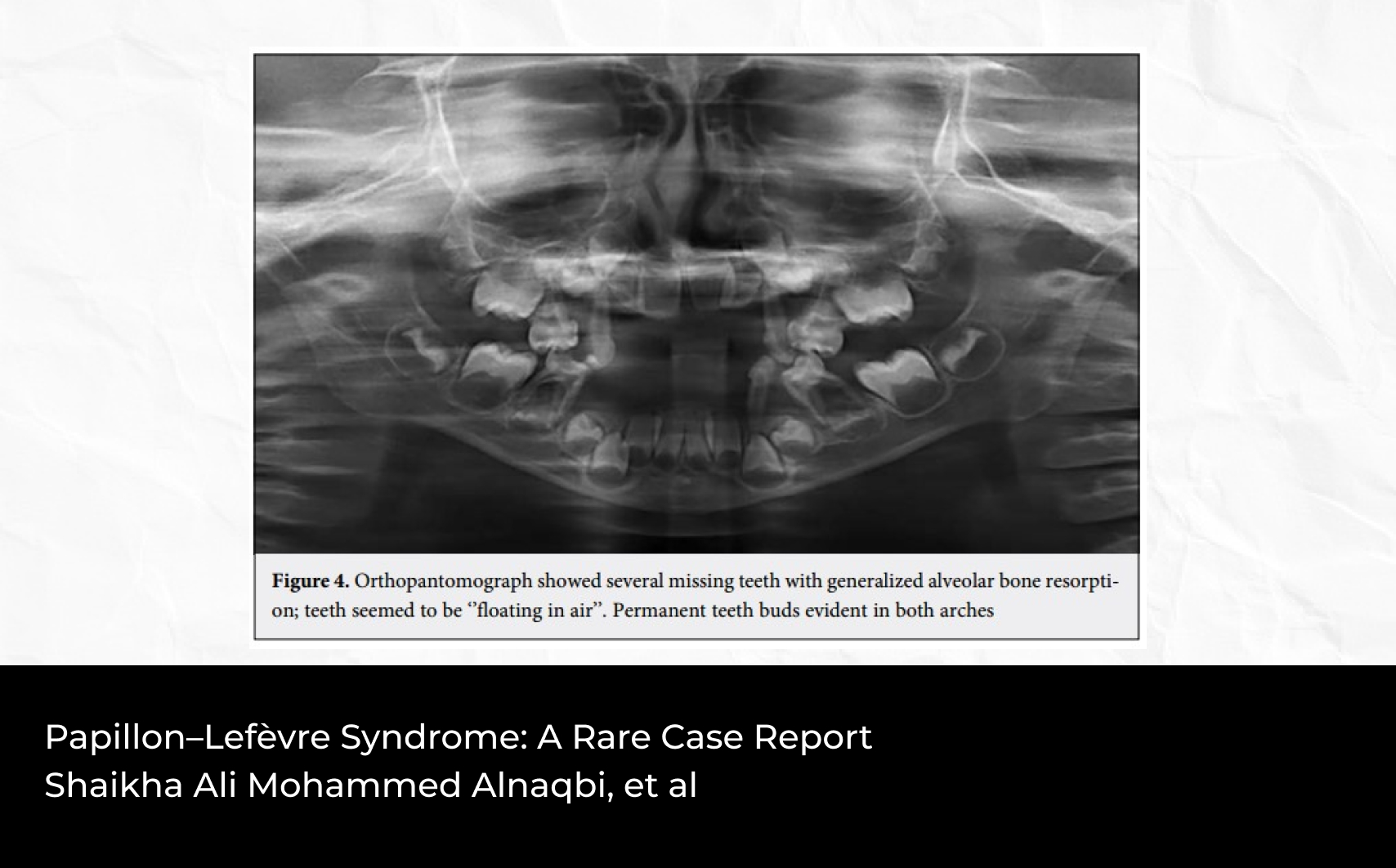
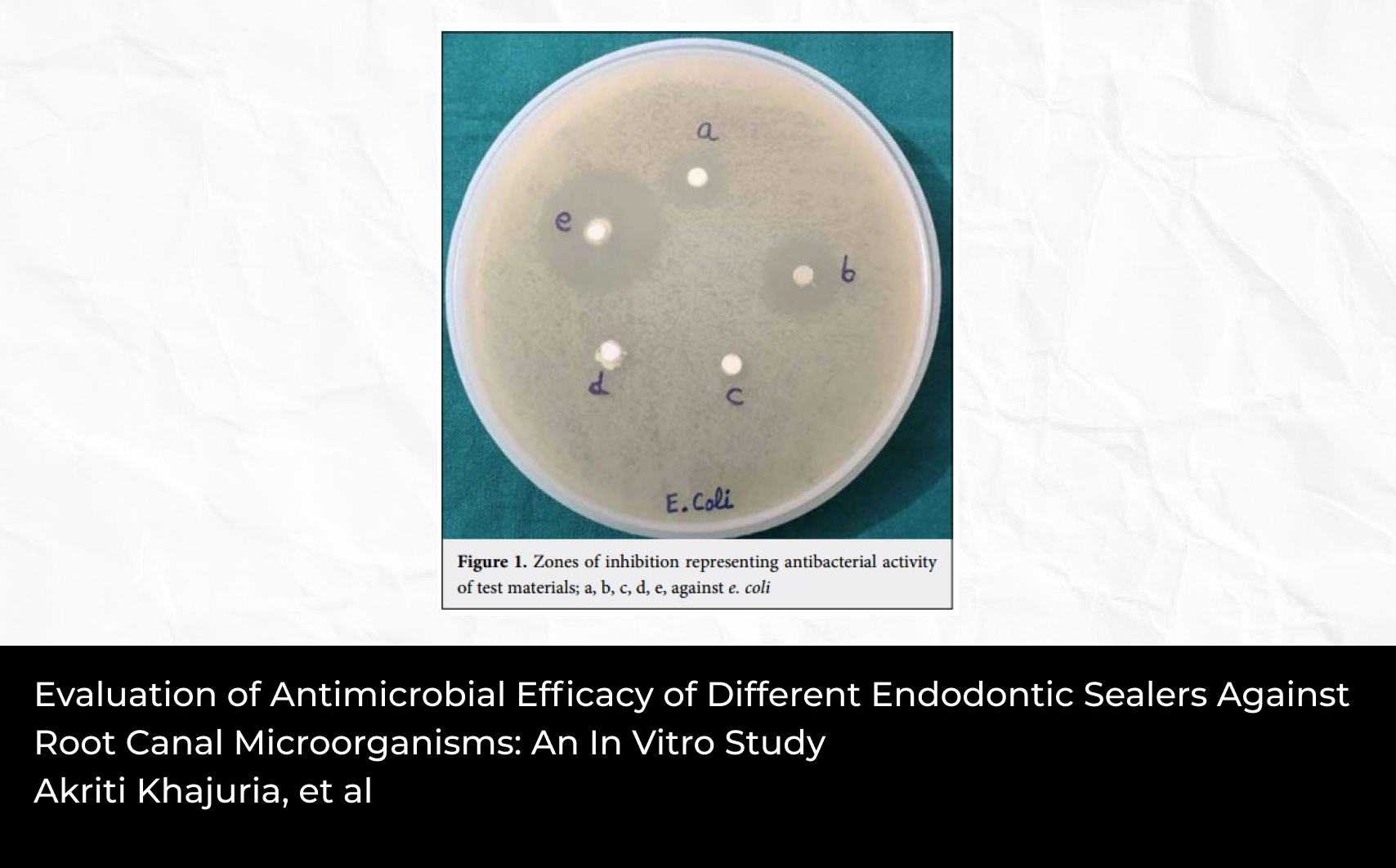
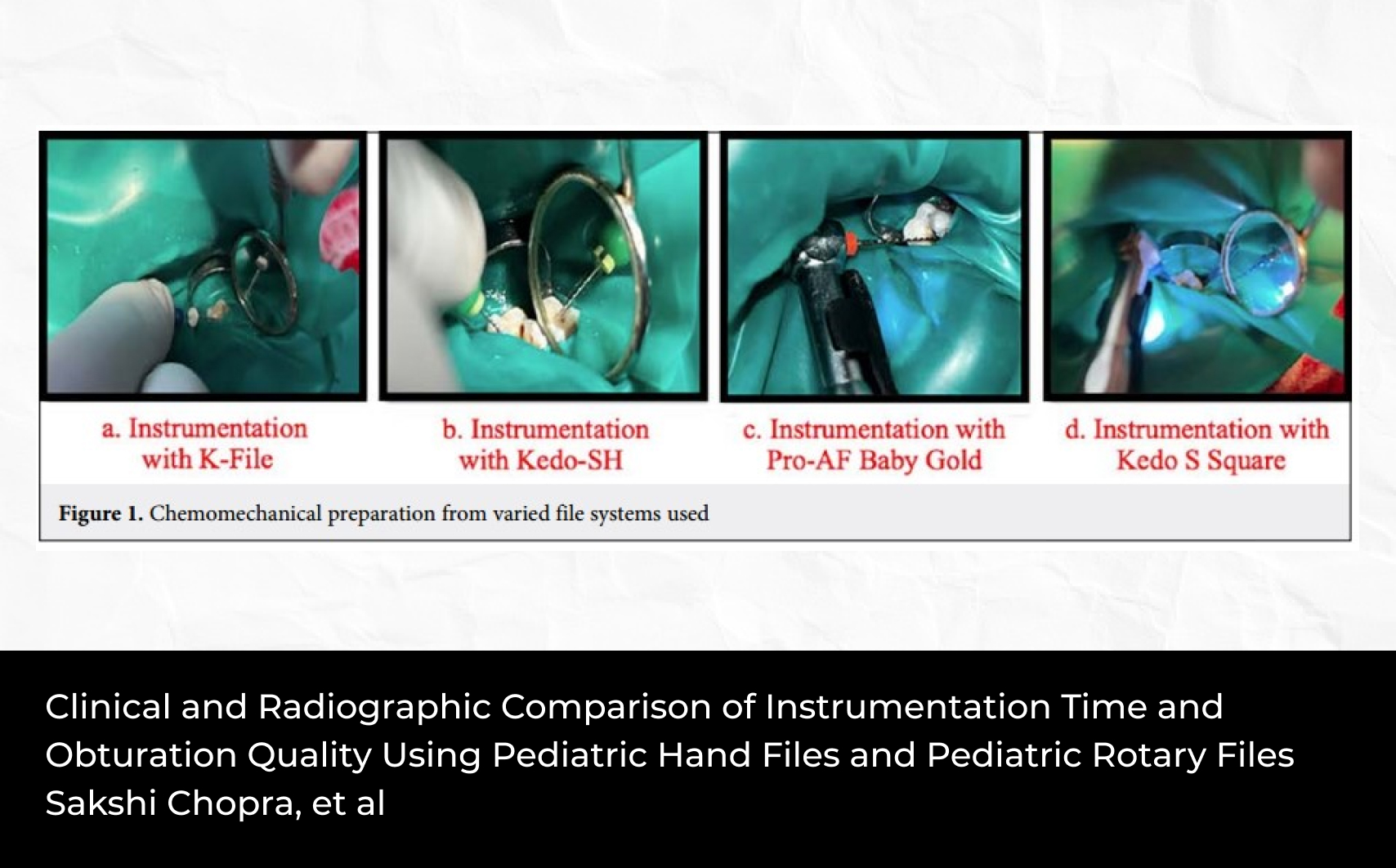
2Department of Operative Dentistry, Faculty of Dentistry, King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia; Department of Conservative Dentistry, Faculty of Dentistry, Alexandria University, Alexandria, Egypt
3Department of Pediatric Dentistry, Faculty of Dentistry, King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia; Department of Pediatric Dentistry and Dental Public Health, Faculty of Dentistry, Alexandria University, Alexandria, Egypt
Abstract
Laser technology offers minimally invasive, painless alternatives to the conventional ways of performing many hard and soft tissue procedures in dentistry. Pediatric dentists should learn the new, less invasive technologies, and adopt them in their routine practice. This article aimed to review the clinical applications of erbium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet (Er:YAG) lasers in pediatric dentistry. An electronic search of databases including Scopus, Science Direct, PubMed, ProQuest, Medline, and Google Scholar databases identified articles published from 1996 to 2020 that described the potential and clinical applications of Er:YAG laser in the pediatric dentist’s practice. The literature shows that Er:YAG laser can accomplish a wide variety of dental procedures with minimal pain and while reducing the risk of infection and bleeding. In clinical studies, patients prefer lasers over conventional methods. Er:YAG laser is preferred among pediatric dentists because it is suitable for both hard tissue and soft tissue procedures.